Lab 10: Request Line
Web-CAT: Submit Python programs to this automated grading platform.
Task Outline
- Due Date: Friday, November 29, 2019
- Total Points: 10
- Implement a
Pythonprogram that determines the validity of an HTTP request line.
Background Theory
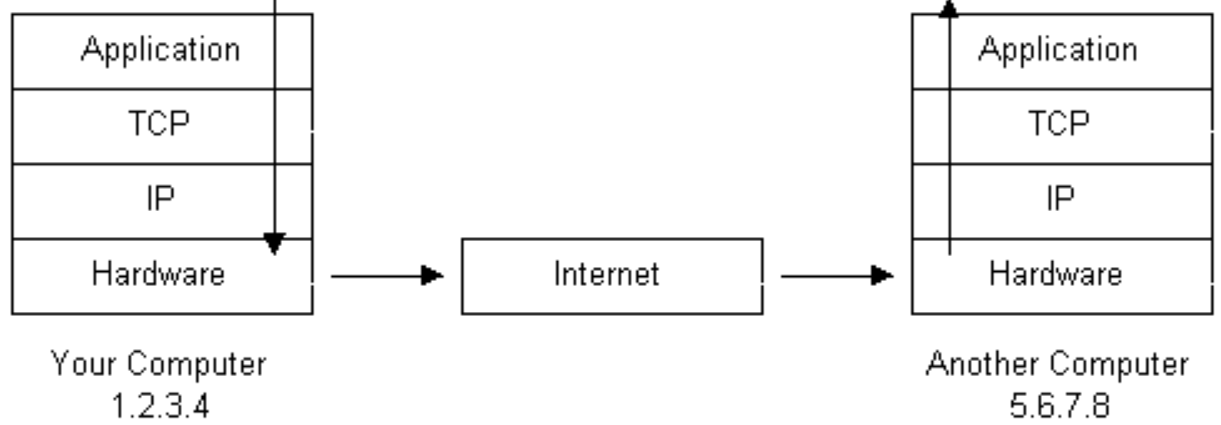
- HyperText Transfer Protocol(HTTP) is the protocol that web browsers and web servers use to communicate with each other over the Internet.
- HTTP is an application level protocol, because it sits on top of the TCP layer in the protocol stack, and it is used by specific applications to talk to each other. In this particular case, those applications happen to be web browsers and web servers.
- HTTP is a connectionless, text-based protocol, in which clients send requests to servers.
- When you type a URL into a web browser, the following steps occur:
- If the URL contains a domain name, then the browser first connects to a Domain Name Server, and retrieves the corresponding IP address for that domain name.
- The web browser then connects to the web server, and sends an HTTP request for the desired web page. The HTTP request takes the following form:
GET /hello.html HTTP/1.1 - The web server receives the request, verifies that it is properly formatted, and returns an appropriate error message if it is not. Then, it checks for the desired web page. If the requested page exists, then the web server sends it out. However, if the web server cannot find the requested web page, then it will send out an error message.
Example Case
- According to Regulation
rfc7230from the Internet Enginering Task Force(IETF), a well-formed HTTP request line takes the following form:
delivery-method SPACE request-target SPACE HTTP-version
- Your task is to verify that a given HTTP request conforms to this structure, and is consistent with the following rules:
- If
delivery-methodis notGET, then the function should return:405 Method Not Allowed - If
request-targetdoes not begin with a/, then the function should return:501 Not Implemented - If
request-targetcontains a", then the function should return:400 Bad Request - If
HTTP-versionis notHTTP/1.1, then the function should return:505 HTTP Version Not Supported
- If
- If none of the above errors occur, then this means that the HTTP request line is well-formed, and that the
parse()function should return therequest-target.
Hints
- You should use string slicing to separate the different parts of the request line. However, this means that you will need to discover the index locations of the
SPACEs. - Use the
find(item)function to discover the index of the firstSPACE, and then usefind(item, startindex)to discover the index of the otherSPACE.
Code Distribution
| Description | File Size | File Name |
|---|---|---|
Python Source Code for Request Line |
1.3KB | lab10.zip |
Contents of lab10.zip:
Lab10RequestLine/
├── requestline.py
└── testrequestline.py
Specification
- Write a
Pythonprogram in the filerequestline.pythat determines the validity of an HTTP request line. - You will write your solution in a function called
parse(line)right below the place where it says:YOUR CODE HERE - When the function call
parse("GET /hello.html HTTP/1.1")is executed, the output of the program should be:/hello.html
Testing
- Run the file
testrequestline.pyto execute thePyUnittest bench.PyUnitindicates a successful test with anOKoutput, and an unsuccessful test with aFAILoutput.
Submission
- Upload the file
requestline.pyto the Web-CAT automated grading platform.